


Machining vs Milling
Overall, machining is an umbrella term covering various techniques used for shaping materials, usually metals and plastics, by removing unnecessary material. It includes processes such as turning, grinding, drilling, and particularly milling. On the other Hand, milling is a machining process that utilizes rotary cutters for removing material from a work piece at an angle to the machine’s axis. This post is going to explain the variations between machining and milling and share information regarding their features, and applications.
Understanding Machining
Machining is a manufacturing process that entails removing material from material to achieve a desired shape. It is a reductive process, which means it cuts away material to form the final piece. The common types of machining processes are as follows:
Turning: Involves rotating the material while a cutting tool moves linearly for removing material. It is generally used for producing cylindrical parts.
Drilling: Uses a spinning drill-bit for creating round holes in a work piece, making holes for fasteners or other pieces.
Grinding: Utilizes an abrasive wheel for removing material and attain a high surface finish or close tolerances, usually used for finishing processes.
Milling: Utilizes rotary cutters for removing material, allowing for a broad range of shapes and intricate geometries. Basically, milling rotates the cutters, not the other way around, in comparison to turning. Machining is crucial in manufacturing as it creates high-precision components with close tolerances and outstanding surface finishes. Apart from its application in bulk production, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is widely used in quick prototyping and reduced-volume production for customized parts.
Understanding Milling
Milling is a distinct type of machining technique that involves utilizing rotary cutters for removing material from a work piece. Milling varies from other machining processes as its tool moves along with the work piece. Allowing the creation of intricate curves, shapes, and surfaces. Milling can work on a lot of materials, such as metals, plastics, and aggregate, which makes it adaptable in many sectors. It has a lot of different operations, like end milling, face milling, and grooving. Eli Whitney first invented the milling machine in the early 1800’s, the start of milling history. This machine was designed for producing exchangeable parts for firearms. It altered manufacturing by making it more accurate and efficient. Eventually, milling technology has evolved considerably, with progression in CNC technology in the late 20th century, therefore turning milling into a highly automated and accurate process. CNC milling machines can make complex parts with little to no human intervention, increasing productivity and regularity. Key Differences Between Machining and Milling Machining and milling are both vital in the manufacturing process, nonetheless, they differ considerably in scope, how they operate, equipment, and material removal methods.
Applications for Machining and Milling
Machining and milling are vital in various sectors because of their ability to produce accurate and intricate components. Sectors that rely heavily on these processes include aerospace, electronics, automotive, medical devices, and manufacturing, to name a few.
- Aerospace: In aerospace industries, machining is vital for producing highly accurate components like turbine blades, parts for engines, and structural parts. Milling is specifically used for creating intricate geometries and detailed characteristics required for aerodynamics and performance.
- Electronics: In electronics, machining is utilized to manufacture housings, heat sinks and connectors. Milling is usually applied for creating intricate enclosures that require accurate dimensions and high surface polishes.
- Automotive: The automotive industry utilizes machining to manufacture engine blocks, transmission parts, and intricate components such as shafts and gears. Plastic parts and automotive body panels are shaped utilize milling methods.
- Medical Devices: The medical sector depends on machining to create surgical instruments, prosthetics, and implants. Milling is necessary for crafting intricate shapes required in custom implants and dental tools.
- Manufacturing: General manufacturing utilizes machining for dies and tool making, creating jigs, prototypes, and fixtures. Milling is helpful for creating dies and molds with intricate contours and cavities.
East Valley Precision – Custom Machinery Specialists
East Valley Precision offers custom CNC Machining in the Chandler, Arizona and surrounding areas. When you need precision CNC machining and milling contact East Valley Precision. Call us at 480-288-6601 for more information or use our form for a quote.

Difference between a CNC Machine and a Lathe Machine
CNC Machine vs. Lathe Machine: Key Differences
Both CNC machines and lathe machines are used for metal and wood cutting, but they have key differences in operation, automation, and capabilities.
1. CNC Machine (Computer Numerical Control Machine)
🔹 Fully automated machining controlled by computer programs.
🔹 Can perform multiple functions (cutting, drilling, milling, engraving, etc.).
🔹 Works on 3-axis, 4-axis, or even 5-axis for complex designs.
🔹 Used in mass production and high-precision industries.
✅ Pros:
✔ High precision and repeatability.
✔ Can produce complex shapes with minimal manual labor.
✔ Works on various materials (metal, plastic, wood).
✔ Faster production with automated programming (G-code).
❌ Cons:
❌ Expensive compared to manual machines.
❌ Requires skilled operators to program and troubleshoot.
💲 Cost Range: $10,000 – $500,000+ (depending on complexity).
2. Lathe Machine (Manual or CNC)
🔹 Primarily used for turning and shaping cylindrical objects.
🔹 Rotates the workpiece while a cutting tool removes material.
🔹 Common for shafts, rods, and symmetrical components.
🔹 Can be manual (operated by hand) or CNC-controlled.
✅ Pros:
✔ Best for cylindrical or round parts.
✔ Easier to operate compared to CNC milling machines.
✔ Lower cost than full CNC machines.
❌ Cons:
❌ Limited to turning operations (doesn’t handle complex shapes like CNC mills).
❌ Manual lathes require skilled labor for precision work.
💲 Cost Range:
- Manual Lathe: $1,000 – $10,000
- CNC Lathe: $20,000 – $100,000+
Key Differences
| Feature | CNC Machine | Lathe Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Computer-controlled | Manually operated or CNC-controlled |
| Operations | Cutting, milling, drilling, engraving, etc. | Mainly turning (cylindrical shaping) |
| Precision | Very high | Moderate (manual), High (CNC lathe) |
| Production | Best for mass production | Best for custom or low-volume work |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
Which One Should You Choose?
✔ Need high precision & automation? → CNC Machine
✔ Working on cylindrical parts? → Lathe Machine
✔ Mass production & complex shapes? → CNC Machine
✔ Small workshop or custom metalworking? → Lathe Machine
East Valley Precision – Custom Machinery Specialists
East Valley Precision offers custom CNC Turning in the Chandler, Arizona and surrounding areas. When you need precision CNC turning and milling contact East Valley Precision. Call us at 480-288-6601 for more information or use our form for a quote.
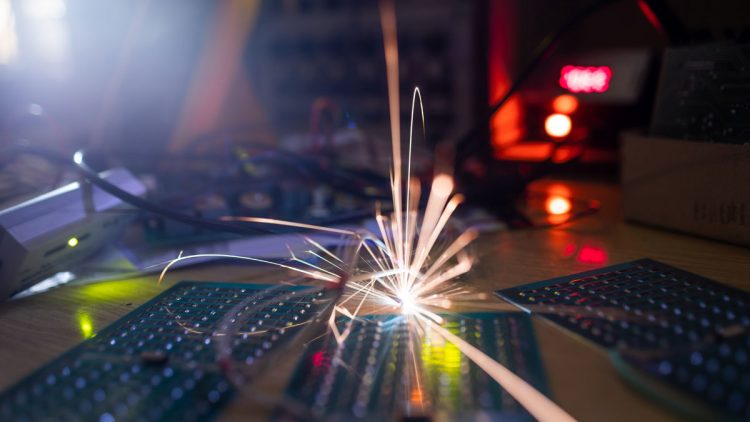
What is Wire EDM?
What is Wire Electrical Discharge Machining?
Wire electrical discharge machining (Wire EDM) utilizes a metallic wire for cutting or shaping workpieces, usually conductive materials, with a thin electrode wire that tracks a specifically programmed path. Usually, the electrode widths vary from .004″ to .012″, nevertheless smaller and larger widths are ready for use.
Throughout the wire cutting process there isn’t any direct contact between the wire and the work piece allowing for machining without causing any deformation in the wires path, or the shape of the material. For accomplishing this, the wire is quickly charged to a required voltage. The wire is also encompassed by deionized water. As the voltage reaches the proper degree, a spark hops the gap and melts a minute part of the work piece. The water cools then removes the minute leftovers from the gap.
The solidity of the work piece material has no damaging impact on the cutting speed. Blanking punches and extrusion dies are frequently machined via wire cutting.
The Way Electrical Discharge Machining Works
The primary EDM process is quite basic. A spark is created between 2 electrodes. The tool electrode is usually known as the electrode, and the work piece electrode as the work piece. The spark is visual evidence of the stream of electricity. This electrical spark produces intense heat with temperatures hitting 8,000 to 12,000 degrees Celsius, melting/vaporizing just about any conductive material. These swift, recurring electrical current discharges happen in a very tiny gap between the 2 electrodes, in which never come in contact with one another. The spark gap is managed by adaptive device controls to guarantee a continual, balanced distance as the electric discharge happens up to millions of times every second.
The spark is very specifically managed and restricted, so it only impacts the face of the material. This process typically does not impact the heat treat underneath the face. Both the tool and workpiece are immersed in dielectric (un-conductive) fluid, usually deionized water.
The spark always happens in the dielectric fluid. The conduction of the deionized water is cautiously overseen, creating a perfect setting for the EDM process. The deionized water additionally provides cooling throughout the machining process, and eradicates the small, eroded metal fragments.
EDM is considered a non-conventional machining technique since it uses electric discharge for removing material from the work piece. This contrasts with conventional machining techniques like grinding or drilling which use mechanical force for removing material.
What Types of Shapes Can A Wire EDM Machine Produce?
Wire EDM machines are a kind of CNC machine that can move along four independent axis to create taper cuts. For instance, a stamping die can be created with 1/4-degree taper or a mold with 1 degree taper in some areas and two degrees in others accurately. Extrusion dies or horns and nozzles can be cut with continually changing tapers. For instance, an intricate shape on top of the work piece can shift to a simple circle at the bottom.
Uses for Wire EDM Cutting
East Valley Precision’s wire cut EDM services are perfect for fragile or small work pieces that might be damaged throughout traditional machining or other conventional methods:
- Thicker parts requiring pristine finishes and/or accuracies.
- Intricate shapes or slender slots
- Large components that need to hold accurate allowances
- Fragile, hard, exotic/costly or weak materials
East Valley Precision – Custom Machinery Specialists
East Valley Precision offers custom CNC Turning in the Chandler, Arizona and surrounding areas. When you need precision CNC turning and milling contact East Valley Precision. Call us at 480-288-6601 for more information or use our form for a quote.

What is а CNC Lathe?
A CNC lathe is a complex machine device intended for precision Computer Numerical Control manufacturing and turning by way of CNC.
It’s a personification of technological development, merging the age-old principles of a lathe machine with state-of-the-art computer programming to reach unparalleled efficiency and accuracy in machining.
The CNC lathe machine device has changed how materials are handled, making it an essential tool in various sectors and many machine shops across the world. Its capability to perform complex shaping and cutting with unbelievable precision makes it a foundation in current manufacturing processes. Whether it’s wood, metal, or plastic, the CNC lathe’s adaptability in handling various materials is unparalleled.
How Does a CNC Lathe Machine Work?
Getting into the inner workings of a CNC lathe uncovers a balance of computerized control and precision engineering. Different from a manual lathe, where the handiwork lies mainly in the hands of its operator, a CNC lathe incorporates computerized technology to improve precision and proficiency. Below is an in-depth look at its process:
Design Phase: To begin with, you, the operator, creates a meticulous design utilizing CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This design comprises of all specifications for the desired piece, from shapes to dimensions.
Programming: Your CAD design is then converted into G-code, the programming language that the CNC machine understands. This code gives instructions to the CNC lathe on how to move, shape, and create the piece.
Setup: After that, you configure the CNC lathe. This involves choosing and installing the proper cutting tools and fastening the workpiece onto the machine.
Machining Process: The CNC lathe, activated by the G-code, starts the machining process. The workpiece is spun at high speed while the cutting tool is moved across two or more axis to shape the piece.
Quality Inspected: During the process, the CNC lathe oversees the cutting environments and makes real-time modifications to guarantee precision. The final piece is inspected against the original specifications for preciseness.
What are the differences between horizontal and vertical CNC lathes?
The main differences between horizontal and vertical CNC lathes consists in their position and the applications they’re most appropriate for.
Horizontal CNC Lathes:
- Positioning: The spindle in this type of lathe is arranged horizontally, with the workpiece mounted vertically to the axis.
- Processes: Mainly used for longer, cylindrical workpieces.
- Pros: Easier chip withdrawal because of gravity, typically better for heavier and larger pieces.
- Limitations: Might not be suitable for parts with intricate geometries.
Vertical CNC Lathes:
- Positioning: The spindle is oriented vertically, with the workpiece connected to a horizontal chuck.
- Processes: Perfect for heavy, large-diameter, short workpieces.
- Pros: Gravity aids in securing the workpiece, decreasing the need for substantial clamping. Provides better access to the workpiece for certain operations.
- Limitations: Not as productive for long, slender workpieces where gravity can affect accuracy.
East Valley Precision – Custom Machinery Specialists
East Valley Precision offers custom CNC Turning in the Chandler, Arizona and surrounding areas. When you need precision CNC turning and milling contact East Valley Precision. Call us at 480-288-6601 for more information or use our form for a quote.

What is Machining?
Machining is a manufacturing technique in which the desired shape is produced by removing material from a larger piece. It is used for creating finished products and for raw material processes. These processes are also referred to as subtractive manufacturing processes. Complicated parts usually require the use of several machining processes along with each other.
A lot of machining processes have high command over the material removal for maximum accuracy. Just about all materials, including metals, ceramics, wood, plastics, glass, etc., support machining processes.
How Machining Works?
Machining processes are reliant on a machine tool to work on the raw material to create the wanted shape. Today’s machine tools are mainly automated. They use built-in computing to translate the commands and work on the piece. The technique of commands is subject to the type of technology that the machine uses. A lot of current machining tools are based on Computer Numerical Control (CNC), in which utilizes CAM programming.
Various Phases of Machining Processes
Machining processes go through several phases to complete the pieces production. These various stages are:
Designing Piece: For machine-driven production using a CNC machine, a graphic design of the piece is created. It then gets saved as a Computer Aided Design (CAD) file. Minute adjustments and hand-operated machining may not require designs.
Creating Computer Aided Manufacturing File: The CAM file includes the G-code that the machine can comprehend. The programmer transforms the CAD file into CAM form. An operator then loads the file into the machine. For a machine that doesn’t have CNC, the CAM file is not required.
Machine Configuration: Each machine requires to be configured before initiating the machining process. Configuration includes loading the piece, adjusting the machine settings, and guaranteeing tight connections.
Machining: The machine starts initiating once the configuration is complete. The configuration is done in front of an operator.
Removal: The finished piece is then removed from the machine. It is then sent for secondary assembly or added machining processes as required.
Different Types of Machining Operations
The extent of applications of the machining process have led to the advent of many kinds of machining processes and operations. The following eleven most notable machining kinds are:
- Milling
- Boring
- Broaching
- Drilling
- Grinding
- Turning
- Reaming
- Planing
- Sawing
- Water Jet Cutting
Learn more about the types of machining operations
Advantages of Machining
A typically asked question concerning machining is ‘Does machining come with any advantages?’ Assessing the advantages of machining turns even more prevalent when considering the close competitiveness with additive manufacturing methods. Below are some of the advantages that machining provides:
Unlimited Materials:
Machining methods can work on all kinds of materials. This is a significant advantage over additive manufacturing methods which work only on a restricted set of materials.
Surface Finish:
The machining process produce a very smooth surface on the work piece. An even further smoothness can be attained with processes such as grinding. Processes such as etching can further push the boundaries of what is possible in surface finishing terms.
Precision:
CNC machining provides some of the most minute tolerances in industrial manufacturing methods. In A lot of CNC machining processes falls under the umbrella terminology of ‘precision machining’. These tolerances could be as low as +/- 0.001″.
Rate of Production:
CNC machining are high-speed processes. As a result, it can easily fulfill the need of mass production. In addition, methods such as multi-axis machining further speeds up the rate of production.
Consistency:
The machining process is highly dependable in terms of results. Consistency is a significant requirement for most sectors. Machining methods always produce matching parts.
Less Labor Intensive:
CNC machines are highly automated devices. It unburdens most of the human labor for other high-priority duties. CNC machines generally require labor only for loading and un-loading of pieces. Other than that, only one operator is adequate to manage the machine operations.
East Valley Precision – Custom Machinery Specialists
East Valley Precision offers custom CNC Turning in the Chandler, Arizona and surrounding areas. When you need precision CNC turning and milling contact East Valley Precision. Call us at 480-288-6601 for more information or use our form for a quote.
